

Out of these, the preferred chemistry for electric vehicles is a combination of lithium, nickel, manganese and cobalt (NMC) due to its low self-heating rate.

The difference lies in the compositions of other metals in the cathode, which could include cobalt, nickel and graphite, depending on the type of application the battery is used for. There are now six types of Li-ion chemistries, all of which use lithium as a key ingredient. Like all technologies, the Li-ion battery has evolved over the years, incorporating new chemistries for different applications and increased performance.
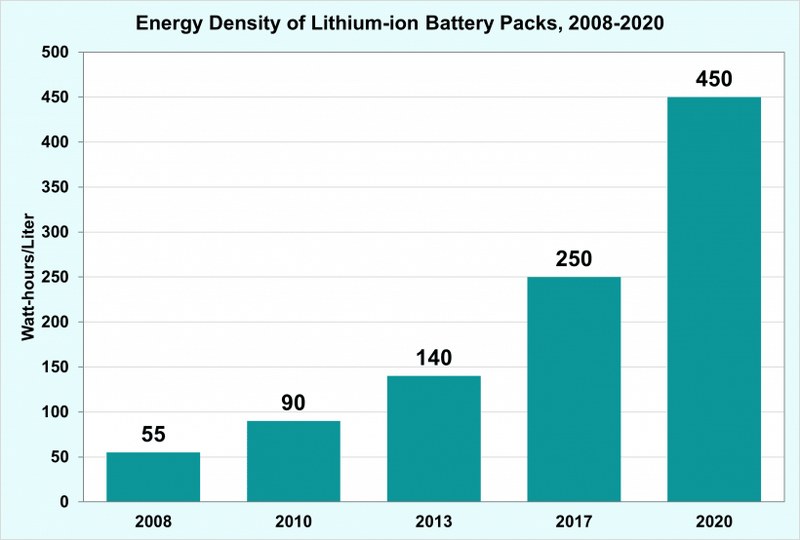

From a clean energy perspective, it has become the ideal fuel source for electric vehicles, which are on their way to dominate our roads for generations to come.
#Lithium ion battery overview portable
There is also no memory effect, a detrimental process where repeated partial discharge/charge cycles can cause a battery to ‘remember’ a lower capacity.Īll of these present significant advantages over Ni-Cd batteries, thus making Li-ion the battery of choice for today’s portable electronics and power systems. Li-ion batteries are comparatively low maintenance and require no scheduled cycling to maintain battery life. In addition, Li-ion battery cells can deliver up to 3.6 volts, 3 times higher than technologies such as Ni-Cd. At about 100-265 Wh/kg, the energy density of lithium-ion is typically twice that of the standard nickel-cadmium batteries. Yoshino, Goodenough and Whittingham were later awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2019 for their pioneering work in this field.įor many years, nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) had been the only suitable battery for electronic equipment, but the rise of lithium-ion technologies in the 1990s proved that it’s possible to use an even lighter and higher quality rechargeable battery in our portable devices.Īs the lightest metal, lithium has the greatest electrochemical potential and provides the largest energy density for its weight. When plugging in the device, the opposite happens: Lithium ions are released by the cathode and received by the anode.Īn illustration of John Goodenough’s early battery designĪ prototype Li-ion battery was first developed by Akira Yoshino in 1985, based on earlier research by John Goodenough, Stanley Whittingham, Rachid Yazami and Koichi Mizushima. The separator blocks the flow of electrons inside the battery.ĭuring a discharge cycle, the anode releases lithium ions to the cathode, generating a flow of electrons from one side to the other. The electrical current then flows from the positive current collector through a device being powered (cell phone, computer, etc.) to the negative current collector.
#Lithium ion battery overview free
It is the movement of lithium ions that creates free electrons in the anode, producing a charge at the positive current collector. The separator, which is located between the anode and cathode and is micro-permeable, allows the lithium ions to pass through due to their small size. The anode and cathode are used to store the lithium, while the electrolyte carries ionized lithium atoms from the anode to the cathode, and vice versa. This kind of battery uses lithium ions as a key component of its electrochemistry, hence its name.įor starters, a battery consists of an anode, cathode, separator, electrolyte and two current collectors (positive and negative). It is also growing in popularity for military and aerospace applications. A lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery is a type of rechargeable battery technology that is found throughout portable electronics and electric vehicles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
